This article delves into the practical implementation of Spring Gateway, offering insights and guidance on how to leverage this technology to enhance your microservices architecture. We will explore real-world examples, demonstrating how Spring Gateway simplifies communication between microservices, improves system resilience, and contributes to the overall agility of your application.
We’ll create a gateway application and 2 web applications namely Student application and college application. Whenever we’ll call the student application using /student endpoint in the url, the gateway will redirect to student service and similarly gateway will redirect to college application when we call the /college endpoint.
STUDENT APPLICATION:
DEPENDENCY:
We can create a new spring project from site: start.spring.io with the following dependencies:
STUDENT POJO:
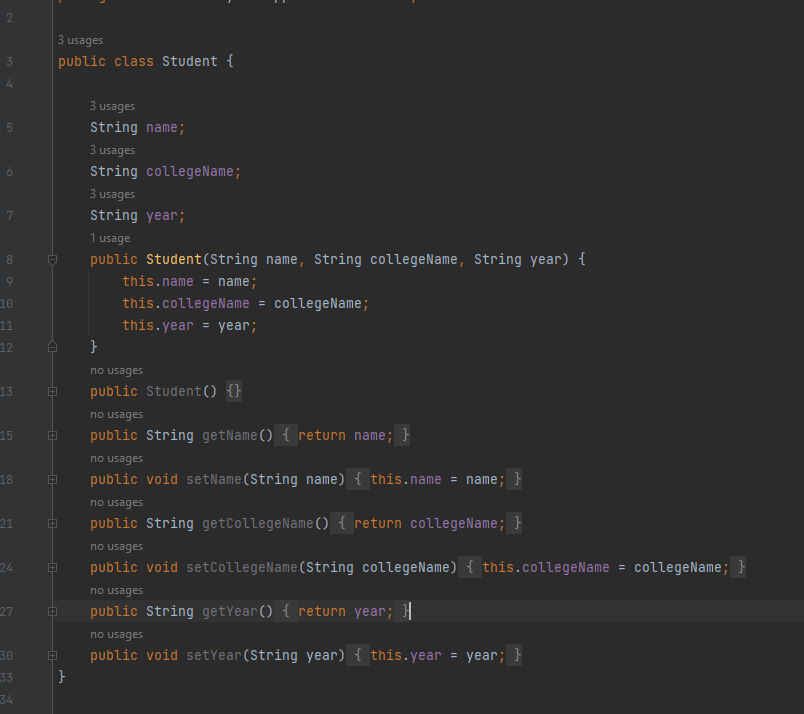
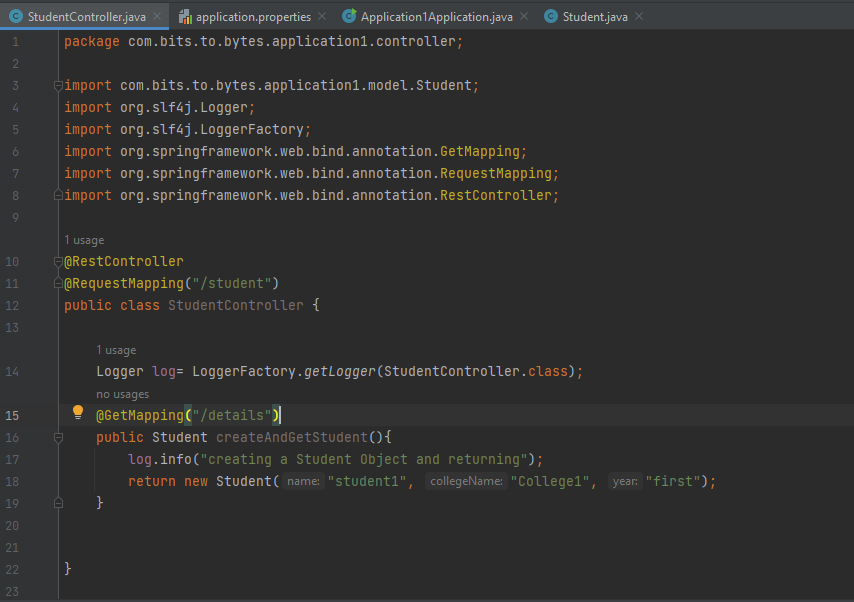
STUDENT CONTROLLER:
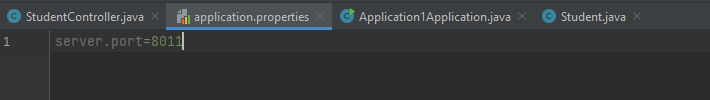
STUDENT PROPERTIES:
COLLEGE APPLICATION:
DEPENDENCY:
COLLEGE POJO:
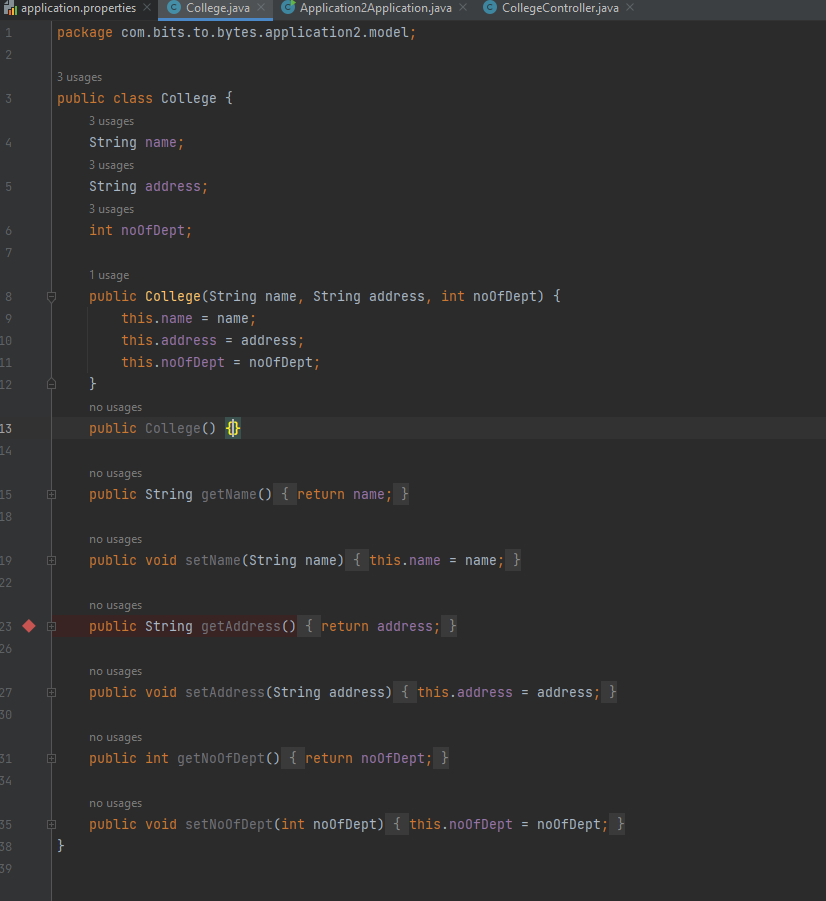
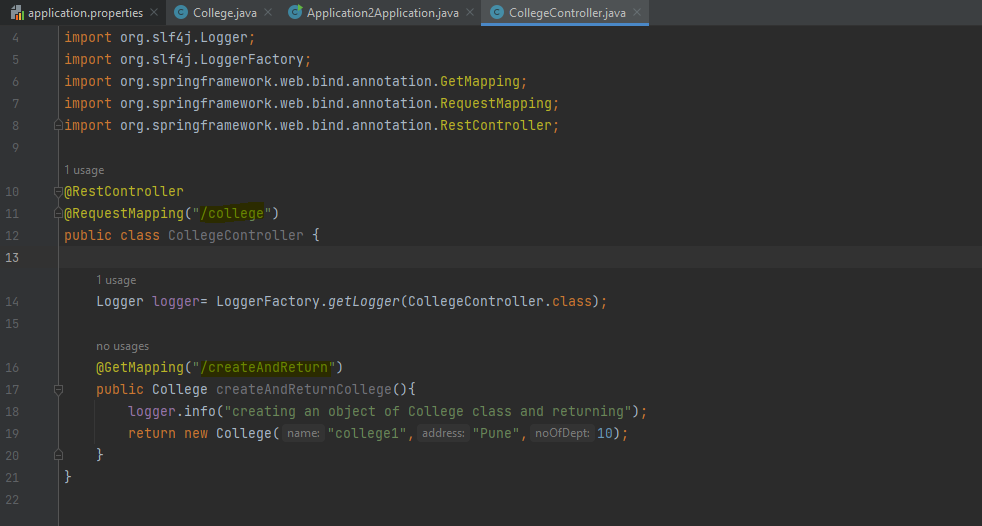
COLLEGE CONTROLLER:
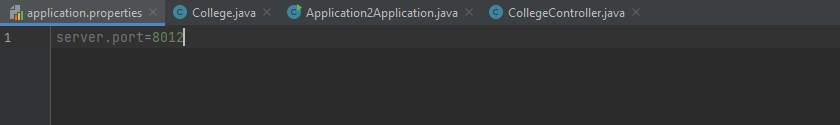
COLLEGE PROPERTIES:
SPRING GATEWAY APPLICATION
DEPENDENCY:
We can create a new spring project from site: start.spring.io with following dependency:
ANNOTATION FOR DISCOVERY:
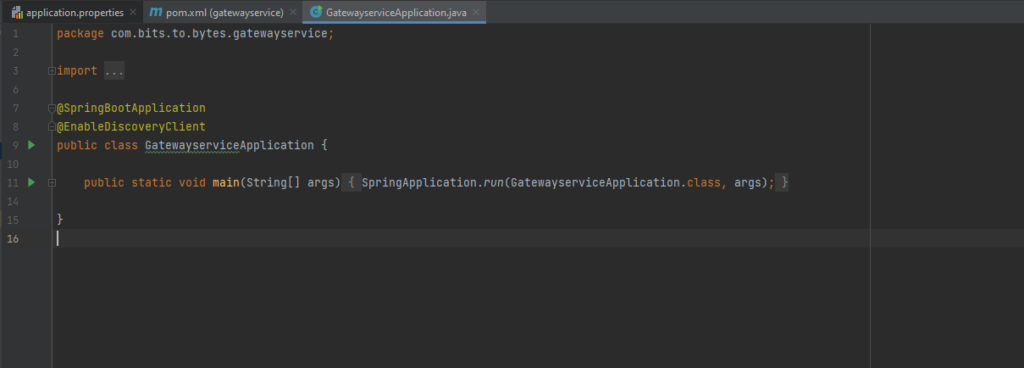
ROUTES SPECIFICATION:
TESTING:
CALL STUDENT details endpoint from gateway:
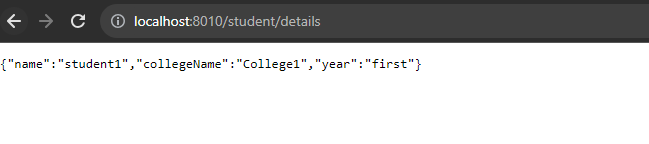
Note the 8010 port which we have specified for gateway application. since we are passing /student in the url, the request is getting forwarded to student application.
CALL COLLEGE details endpoint from gateway:
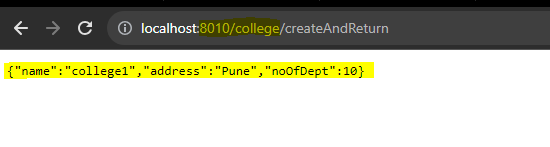
Just like for students, when we pass /college in the url, the request is getting forwarded to college application.